Mastering the Electronic Product Development Process: Partnering with Experts in Design and Manufacturing for Success

The electronic product development process is a complex but rewarding journey. The development process in itself is often a balancing act between innovation, cost management, and technical expertise. This blog explores how partnering with expert design and manufacturing teams can significantly streamline this process, helping you overcome common challenges and bring your product to market faster and more efficiently.
Understanding the Electronic Product Development Process
Launching an electronic product is far more intricate than many realize. It’s a multi-phase journey that requires meticulous planning, testing, and refinement. Let’s break down the key stages in the electronic product development process:
- Concept Development: Before a single component is designed or manufactured, the concept phase is where your product vision is shaped. Questions like “What does the product do?” and “Who will use it?” must be answered. This phase defines the product’s target audience, features, and problem-solving capabilities.
- Design and Engineering: In this phase, detailed prototypes and designs come to life. Electronic components, particularly the printed circuit board (PCB), are carefully designed to meet the product’s functionality and market demands. Collaboration with a design team ensures the final product is both innovative and technically sound.
- Testing and Validation: Ensuring the product functions as expected is critical. Various tests such as EVT (Engineering Validation Test), DVT (Design Validation Test), and PVT (Production Validation Test) are conducted to identify and address potential issues before the product moves into full-scale manufacturing.
Each phase must work in harmony to ensure the product development process flows smoothly. Most importantly, collaboration with design and manufacturing experts during each stage can ensure that costly mistakes and delays are minimized.
Why Collaborating with Design and Manufacturing Partners Matters
In the highly competitive electronics industry, working in silos rarely leads to success. Instead, close collaboration between design and manufacturing partners is critical. Here’s why this partnership can make or break your product:
Expertise at Every Stage
Design partners offer the technical know-how to create an innovative and functional product, while manufacturing partners bring insights that ensure the product is scalable. These partners can foresee potential manufacturing challenges early in the design phase, which can save time and resources in the long run.
Cost Efficiency
One of the most significant advantages of early collaboration is cost savings. Manufacturing experts can help identify cost-effective design solutions, optimize material use, and suggest alternative manufacturing processes that don’t compromise quality but reduce expenses.
Reduced Time to Market
A seamless transition from design to production means that your product can be brought to market faster. By working collaboratively, issues such as production bottlenecks or redesigns are minimized, allowing for quicker prototyping, testing, and eventual mass production.

Working with design and manufacturing partners creates an ecosystem of innovation and efficiency that directly benefits your product’s marketability and profitability.
Step-by-Step Guide to Electronic Product Development and Manufacturing
Electronic product development may seem overwhelming but breaking it down into manageable steps can simplify the process. Here’s a step-by-step guide to streamline your efforts.

Defining Your Product
Before any design work can begin, you need a solid understanding of what you want to build. What problem does your product solve? How does it stand out from competitors? Answering these questions will form the backbone of your development strategy. A deep market analysis at this stage will help clarify user needs, giving direction to your design team.

Partnering with a Design Team
Once the product concept is clear, it’s time to work with a design team. This team will help translate your idea into a working model, focusing on aspects like PCB design, software integration, and user interface. Early-stage testing—Engineering Validation Test (EVT)—is conducted here to ensure that all components work together harmoniously.

Collaborating with Manufacturing Partners
After your design has passed the initial testing phases, it’s time to bring in a manufacturing partner. This partner will refine the design for large-scale production. Design Validation Tests (DVT) ensure that the product can be manufactured at volume without compromising quality. Working closely with your manufacturing partner at this stage will also help optimize production costs.

Testing and Validation
Testing is a continuous process throughout product development. The final Production Validation Test (PVT) confirms that the product can be manufactured at scale and still meet all required specifications. This phase also includes stress tests to ensure durability and functionality under various conditions.
By following these steps and working with expert partners, you’ll navigate the complex development process with greater ease.
The Importance of Prototype Development and Iteration
Prototyping is an essential part of product development. It allows your team to test functionality, gather feedback, and identify potential issues early. But creating one prototype is rarely enough. Iterating through multiple versions helps refine the product, improving both performance and user experience.
- Initial Prototypes often called MVPs (Minimum Viable Products), these early versions of your product are created to validate the concept and key features.
- Refinement after gathering feedback from internal tests or beta testers, you can iterate on the design. This process involves making minor adjustments to address any usability issues, improving the product’s efficiency or manufacturability.
- Final Prototypes are pre-production models used for final validation and testing. They should closely resemble the product that will be manufactured on a large scale.
Each iteration brings you closer to a final product that is not only market-ready but also optimized for manufacturing, cost efficiency, and user satisfaction.
Navigating Regulatory and Compliance Requirements
Before your product can be sold, it must meet various regulatory standards and compliance requirements. These regulations ensure safety and environmental sustainability, among other concerns. Working with partners familiar with industry regulations will save time and avoid costly legal delays.
Some examples of common regulatory standards include:
- UL Certification (for U.S. and Canadian markets): Ensures products meet safety standards, particularly for electrical equipment.
- CSA Certification (for U.S. and Canadian markets): Confirms that products meet the applicable standards for safety and performance ensuring compliance.
- RoHS Compliance: Restricts the use of hazardous materials in electronic products, which is crucial for launching products in various markets.
By understanding and preparing for these requirements early in the design phase, you avoid delays in getting your product to market.
Design for Manufacturability (DFM) and Its Role in the Electronic Product Development Process
Design for Manufacturability (DFM) is a key principle in product design and manufacturing. It involves adjusting the product’s design to make it easier and more cost-effective to manufacture. A product that is difficult or expensive to manufacture will struggle to compete in the marketplace. Examples of DFM principles include:
- Choosing materials that are readily available and cost-effective.
- Ensuring that electronic components can be easily placed during the manufacturing process.
- Designing the product so that it can be assembled with minimal steps, reducing production time.
Working closely with manufacturing partners during the electronic product development process ensures that your product is manufacturable at scale and at the right price point.
Integrating Feedback from Early Users and Beta Testing
Once you have a working prototype, one of the most valuable steps is gathering feedback from real users. Beta testing allows you to identify any unforeseen issues, improve user experience, and fine-tune your product for a better market fit. Collaborating closely with your design and manufacturing partners during this phase ensures that changes can be quickly implemented without disrupting the development timeline.
Why Does Early Feedback Matter?
Gathering input from actual users can highlight usability issues that may not have been caught during internal testing. This feedback helps in refining the product before mass production, ensuring that the final product meets customer expectations.
Iterative Improvement Adds Value
Incorporating feedback into future iterations of your product ensures continuous improvement. Design teams can make the necessary adjustments to hardware, software, or firmware, while manufacturing teams optimize the production process based on this feedback.
By using early-stage feedback, you can reduce post-launch issues and improve customer satisfaction, increasing the chances of your product’s long-term success.
Managing Supply Chain and Logistics in Electronics Manufacturing
Once your product is ready for production, it’s essential to manage the supply chain and logistics effectively. Poor supply chain management can lead to delays, higher costs, or even a halt in production. Working with a manufacturing partner that has a robust supply chain is crucial for meeting delivery deadlines and maintaining product quality.
- Component Sourcing: Electronics manufacturing often requires sourcing components from various suppliers. Ensuring that these components meet quality standards and are available on time is critical. Your manufacturing partner should have strong relationships with reliable suppliers to mitigate the risk of shortages or delays.
- Inventory Management: Efficient inventory management ensures that the right number of components is available when needed. This helps avoid both excess inventory, which ties up capital, and shortages, which can halt production.
- Logistics: Managing logistics, especially when working with international partners, can be challenging. It’s important to have clear timelines for production and delivery to ensure that your product reaches the market on schedule.
By working with a manufacturing partner that has a well-established supply chain, you can reduce risks and ensure a smoother production process.
The Role of Firmware and Software in Electronic Product Development Process
In modern electronic products, firmware and software play just as important a role as hardware. From user interfaces to connectivity features, the software is often the “brain” of the device, determining how it interacts with users and other devices. Coordinating between software developers and hardware designers is crucial for product success.
Firmware is the permanent software programmed into your product’s hardware. It manages the basic functions of the product, such as controlling power and processing inputs. It’s essential to integrate firmware development early in the design phase to ensure compatibility with hardware.
Many electronic products today include apps or other software interfaces. For example, if your product is part of the Internet of Things (IoT), it may need to communicate with other devices or be controlled via a mobile app. Collaborating between software developers and the design team ensures seamless integration of these features.
Firmware and software require rigorous testing to ensure they work reliably with the hardware. After the product launch, updates and bug fixes may be necessary, so planning for long-term support is critical.
Whether your product is a standalone device or part of a broader ecosystem, firmware and software development must be a coordinated effort between your internal teams and external partners.
Cost Considerations: Balancing Quality and Budget
Balancing your product’s quality and budget is one of the most challenging aspects of the electronic product development process. While it’s tempting to cut corners to save costs, doing so can often lead to long-term problems such as increased returns, negative customer reviews, or even product recalls.
Upfront Design Costs vs. Long-Term Savings:
Investing in high-quality design and engineering early in the process can save significant costs down the road. For example, a well-designed PCB may cost more initially but can reduce manufacturing errors and improve product reliability.
Manufacturing Costs:
Mass production can be expensive, so it’s essential to work with your manufacturing partner to optimize production processes. This includes minimizing waste, improving assembly efficiency, and sourcing cost-effective materials without compromising quality.
Testing Costs:
Rigorous testing during the EVT, DVT, and PVT phases adds to the overall cost but ensures that your product performs reliably. Identifying issues before full-scale production can save significant amounts of money compared to fixing problems post-launch.
Striking the right balance between quality and cost is key to the long-term success of your electronic product. By working closely with both design and manufacturing partners, you can create a product that meets market expectations without exceeding your budget.
Case Study: Successful Collaboration with Design and Manufacturing Experts
Let’s look at a real-life example of how collaboration between design and manufacturing experts resulted in a successful product launch.
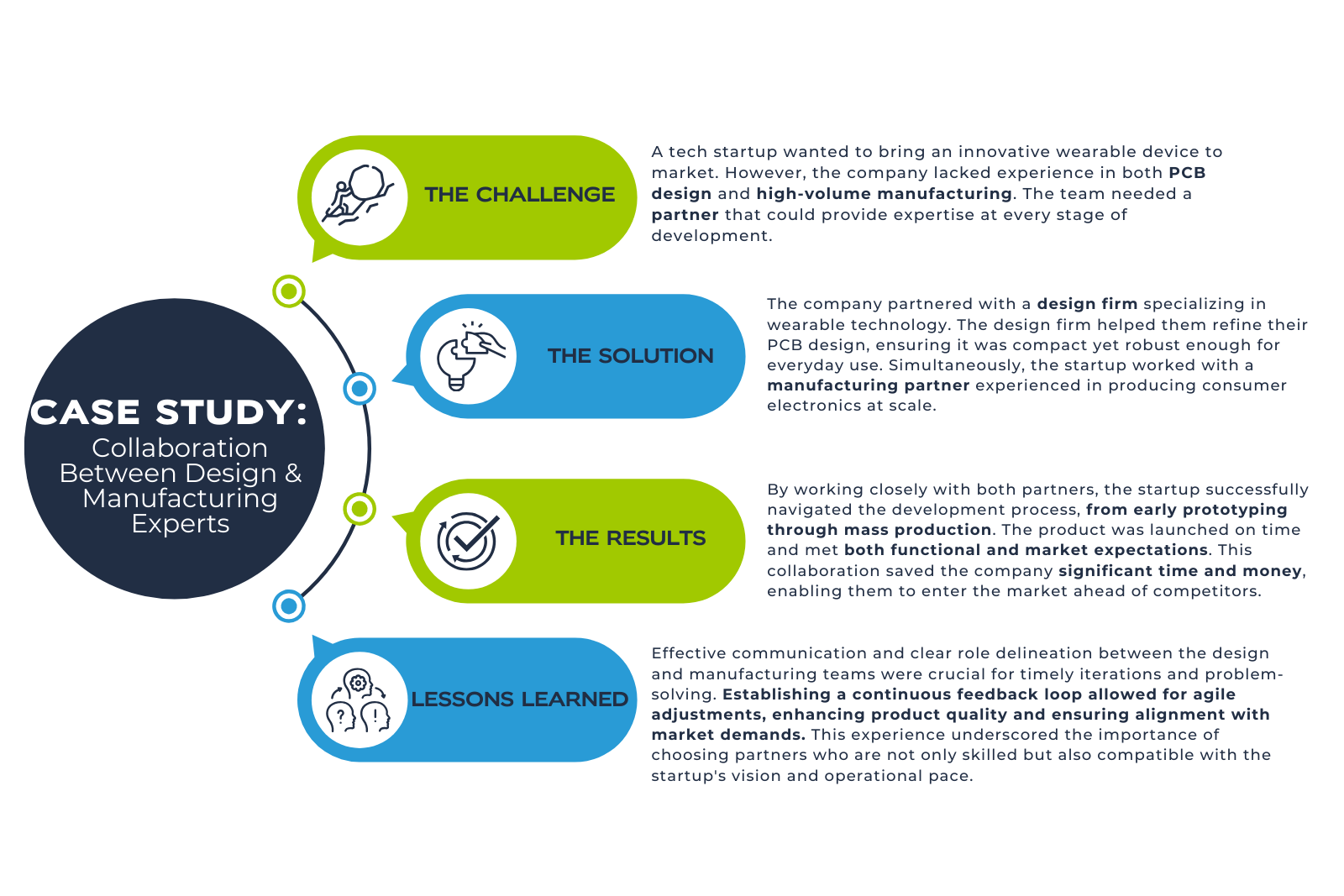
This case study underscores the importance of choosing the right partners and maintaining open communication throughout the development process.
How to Scale Manufacturing While Maintaining Quality
Scaling your product from prototype to mass production is one of the most challenging aspects of the development process. As production scales, maintaining consistent quality across thousands or even millions of units becomes increasingly difficult.
- Implementing strong quality control (QC) measures is critical for ensuring consistency in mass production. This includes automated testing during the manufacturing process, as well as manual inspections for critical components.
- Scaling up production often requires working with multiple suppliers. Maintaining relationships with reliable suppliers ensures that components meet quality standards and are delivered on time. Regular audits of suppliers’ facilities can help mitigate risks related to quality or delays.
- Even after scaling, manufacturers should aim for continuous improvement in both processes and product quality. By collecting data on production performance and customer feedback, you can identify areas for optimization and prevent recurring issues.
Scaling manufacturing doesn’t have to mean sacrificing quality. With careful planning and strong partnerships, you can expand production while maintaining the high standards that your customers expect.
The August Electronics Advantage
At August Electronics, we pride ourselves on being more than just a manufacturing partner—we’re an integral part of your product development journey. Our approach is rooted in collaboration, and we’re fully committed to being an extension of your team. Whether you’re a startup or an established enterprise, we bring our extensive experience and expertise to ensure your product moves seamlessly from concept to market.
While the design phase remains your responsibility, we expertly manage every other aspect of the production process, including quality management systems (QMS), inventory control, logistics, and more. Once your prototype is ready for scaling, our team steps in to ensure an efficient and optimized production process, mitigating costs and delays while maintaining quality at every stage.
One of our key strengths is our North American advantage, with our 85,000-square-foot facility in Calgary, AB. By keeping production domestic, we help clients avoid the complexities and uncertainties of offshore manufacturing. This leads to shorter lead times, better control over quality, control over proprietary information and fewer logistical challenges. Furthermore, the “Made in North America” label adds credibility and ensures your product meets stringent local regulations, which can enhance its market appeal.
Our solutions are flexible and scalable, able to accommodate any industry, product, or challenge. Whether you’re in consumer electronics, industrial automation, or healthcare, our manufacturing capabilities are designed to meet the specific needs of any sector. We are committed to delivering high-quality, custom solutions that align perfectly with your business goals and product demands.
At August Electronics, we make the journey from design to production seamless by providing comprehensive, efficient, and high-quality manufacturing solutions, positioning your product for success from the outset.
Conclusion
Bringing an electronic product to market involves navigating a series of intricate steps, from concept development to large-scale manufacturing. Partnering with expert design and/or manufacturing teams can significantly streamline this process, allowing you to bring innovative products to market faster and more efficiently. By collaborating closely with these experts at each phase—whether it’s design, testing, or production—you minimize costly errors and enhance both the quality and market readiness of your product.
August Electronics excels in providing customized solutions that not only meet industry standards but exceed customer expectations. Ultimately, a strategic partnership can be the key to achieving long-term success, ensuring that your product achieves commercial success while maintaining its innovative edge. With the right approach and expert collaboration, your product can thrive in competitive markets. Contact us to learn more about how we can support your product development journey.
